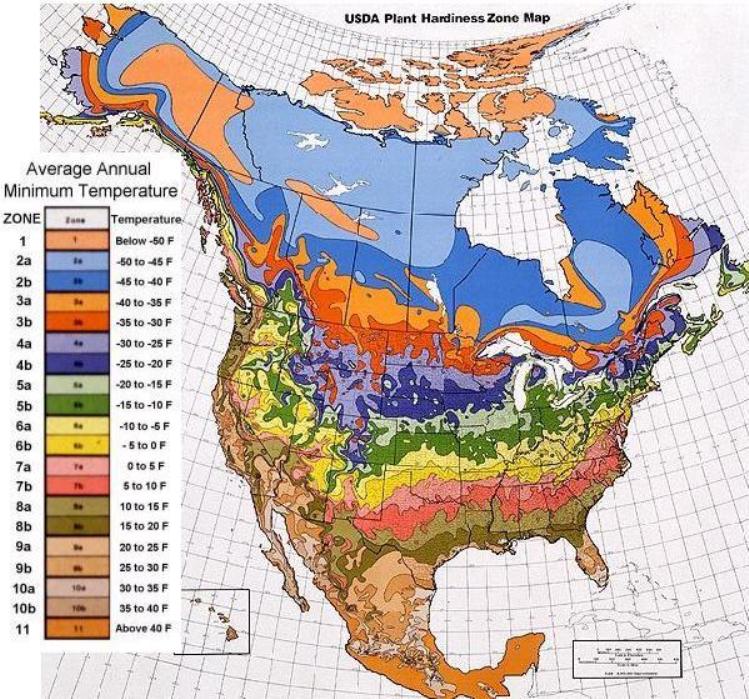
USDA Hardiness Zone Map



Read our reviews at Dave's Garden.
Click Here!
20% Off Your First Order, with First-time Newsletter Subscription!
Sign up for our newsletter and receive a one-time use 20% Off coupon! (Must enter coupon code during checkout to receive discount!)
Click Here to sign up for our Newsletter!
(Coupon not valid on Bulk Seed or Seed Collections. Offer applies only to first-time subscribers.)
